A Debit Put Spread, also known as a Bear Put Spread, is a strategy that involves buying a put option and then selling a put option at a lower strike (deeper out-of-the-money), both for the same expiration. The strategy requires an initial outlay of premium, because the higher strike put will have a higher cost than the lower strike put. It is one of the most common option spreads used by traders with a bearish outlook.
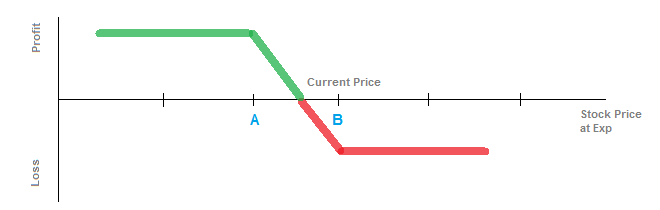
In the diagram above, you'd be buying a put at strike B (near at-the-money) and selling a put at strike A (out-of-the-money). There are many ways to structure the debit put spread, but you are using the sale of the lower strike to partially fund the purchase of the higher put, in order to establish a bearish position.
If the stock price is currently $100, you buy a put on the $100 strike for $4, and you sell a put at the $95 strike for $2. The initial cost of the strategy is $2 ($4 - $2). In order for you to profit from the strategy, the stock price would have to move lower than $98, which is the long strike $100 minus the cost of the spread $2. Your maximum gain would be realized if the stock moves below the $95 strike. There, your put spread would be worth $5 and your cost was $2, netting you a profit of $3.
A debit put spread is a very common spread to use with a bearish outlook. You are expecting the stock to move to the downside, and you're willing to limit your potential gains by selling the out-of-the-money put to offset your costs.
The break-even point is equal to the strike for the long call (strike B) minus the cost of the spread.
The maximum gain is capped at the value of the spread minus the initial cost. If the distance between your two strikes (strike A and strike B) is $5, and the cost is $2, then your max gain is $3. You would achieve the max gain if the stock moves below strike A.
Your maximum loss is the amount you paid for the spread. If the stock at expiration is at or above the long put strike (strike B), then both options would be worthless and you would lose the amount paid.